German forces began the deportation of 440,000 Jews from Hungary in one month. Most of them killed
WW2, WWII, Holocaust.
On March 18, 1944, Hitler summoned Horthy to a conference in Austria, where he demanded greater acquiescence from the Hungarian state. Horthy resisted, but his efforts were fruitless – while he attended the conference, German tanks rolled into Budapest.
On March 23, 1944, the government of Döme Sztójay was installed.
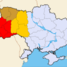
A few days later, Ruthenia, Northern Transylvania and the border region with Croatia and Serbia were placed under military command.
On April 9, Prime Minister Döme Sztójay and the Germans obligated Hungary to place at the disposal of the Reich 300,000 Jewish laborers.
On April 14, Endre, Baky, and SS Obersturmbannführer Eichmann decided to deport all the Jews of Hungary to Germany.
Adolf Eichmann, whose duties included supervising the extermination of Jews, set up plan and deportation was accomplished in less than 8 weeks with the enthusiastic help of the Hungarian authorities, particularly the gendarmerie (csendőrség).
The plan was to use 45 cattle cars per train, 4 trains a day, to deport 12,000 Jews to Auschwitz every day from the countryside, starting in mid-May; this was to be followed by the deportation of Jews of Budapest from about July 15.
The first transports to Auschwitz began in early May 1944 and continued even as Soviet troops approached
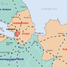
The Hungarian commander of the Kassa (Košice) railroad station meticulously recorded the trains heading to Auschwitz with their place of departure and the number of people inside them.
The first train went through Kassa on May 14. On a typical day, there were three or four trains, with between 3,000 and 4,000 people on each train, for a total of approximately 12,000 Jews delivered to the extermination facilities each day.
There were 109 trains during these 33 days through June 16. (There were days when there were as many as six trains.)
Between June 25 and 29, there were 10 trains, then an additional 18 trains on July 5–9.
The 138th recorded train (with the 400,426th victim) heading to Auschwitz via Kassa was on July 20.
Another 10 trains were sent to Auschwitz via other routes (24,000+ people) (the first two left Budapest and Topolya on April 29 and arrived at Auschwitz on May 2), while 7 trains with 20,787 people went to Strasshofbetween June 25 and 28 (2 each from Debrecen, Szeged and Baja, 1 from Szolnok).
The unique Kastner train left for Bergen-Belsen with 1,685 people on June 30.
By July 9, 437,402 Jews had been deported according to Reich plenipotentiary in Hungary Edmund Veesenmayer's official German reports
***
Jews have a long history in the region now known as Hungary, with some records even predating the 895 AD Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin by over 600 years.
In the first few decades of the 20th century the Jews of Hungary numbered roughly 5 percent of the population. This minority had managed to achieve great commercial success, and Jews were large represented in the professions, relative to their numbers.
In 1921 Budapest, 88% of the members of the stock exchange and 91% of the currency brokers were Jews, many of them ennobled. In interwar Hungary, more than half and perhaps as much as 90 percent of Hungarian industry was owned or operated by a few closely related Jewish banking families.
Jews represented one-fourth of all university students and 43% percent at Budapest Technological University.
In 1920,
- 60 percent of Hungarian doctors,
- 51 percent of lawyers,
- 39 percent of all privately employed engineers and chemists,
- 34 percent of editors and journalists, and
- 29 percent of musicians identified themselves as Jews by religion.
Starting in 1938, Hungary under Miklós Horthy passed a series of anti-Jewish measures in emulation of Germany's Nürnberg Laws. The first, promulgated on May 29, 1938, restricted the number of Jews in each commercial enterprise, in the press, among physicians, engineers and lawyers to twenty percent.
The second anti-Jewish law (May 5, 1939), for the first time, defined Jews racially: people with 2, 3 or 4 Jewish-born grandparents were declared Jewish.
Their employment in government at any level was forbidden, they could not be editors at newspapers, their numbers were restricted to six per cent among theater and movie actors, physicians, lawyers and engineers. Private companies were forbidden to employ more than 12% Jews.
250,000 Hungarian Jews lost their income.
At the next elections, less than a month after this new anti-Jewish legislation, only 38 privileged Jews could vote.
Related events
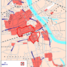
Map
Sources: wikipedia.org, news.lv
No places assigned
Persons
| Name | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | Joseph Goebbels |
| 2 |  | Adolf Hitler |
Cemeteries
| Name | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | Babi Yar |